= BFL)
distance on the optical axis between last active optical surface and the sensor when the object is at infinity.
The value is only valid in paraxial optics, ie for objects close to the optical axis.
Further off the optical axis, the focal distance of distant objects is affected by the spherical aberration.
(back focal distance = Back Focal Length = BFL)
Note:
Not to be confused with the effective focal length EFL!
The difference between the usual color and monochrome – ( ” black and white ” – ) cameras is an additional layer of small color filters , mostly arranged in the so-called ” Bayer pattern ” (patented by Bryce E. Bayer, 1976, employee of Eastman Kodak ) .

See Why can color cameras use lower resolution lenses than monochrome cameras?
= Back Focal Length
= distance between the last optical active surface and the image of objects at infinity that are close to the axis.
A picture taken with a monochrome camera usually has 256 levels of gray.
If the image just has two gray levels, it’s called “binary” image.
An old style fax usually shows a binary image
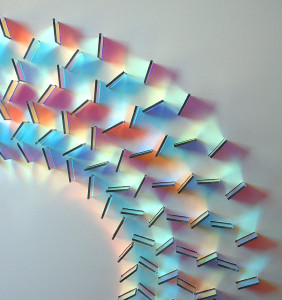
Here’s a wonderful example of Art based on dichroic filters.
We notice that the colors change at different angles of the filters.
Even more visible here :
We notice especially that for filters of the outer circle, filters that have a 90 degree different orientation have about the same color transmission. Especially look at the topmost, the rightmost (both orange colored) and the top-right-most filter (with a purple touch)
Below is a calculator that gives an idea about the resulting interval of wavelengths (called “band” ) when you use the filter at some angle off the designed incident angle.
The filters above seemed designed for an incident of 45 degrees to the surface. Thus +45 and -45 degrees result in the same color and in between we get a blue shift of the wavelength that pass.
The calculation is just for the primitive case of a rectangular transmission curve.
Bokeh is a word that describes blurry, quite large, often round blobs in the image, often as background of some focussed image part.
As an example see the Bokeh of these lights of a Christmas tree.

Bokeh
“Bokeh” actually is the image of typically point sized Objects in a distance far outside the DOF, most often point size objects at infinity while the lens is focussed on some near distance or point sized object in the foreground when the lens is focussed on infinity.
A diagram explains this best :
The lowest large dot on the right is an example for Bokeh.
The shape of the Bokeh is the shape of the physical Iris. This is why many customers prefer round iris shapes

Bokeh of a catadioptric lens (=mirror lens), (C) Wikipedia
The Bokeh has ring shape here, because the image was taken with by a mirror lens, so that the iris center wasn’t exposed to light.