The Diffraction limit describes the maximum possible MTF / resolution that a “perfect” lens could possibly have
Archives
dispersion
(from latin dispergere, “to scatter”, to disperse” ) :
Dependency of a measure on frequency / wavelength.
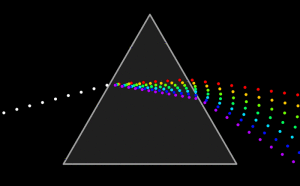 (C) Wikipedia, zum Animieren bitte klicken
(C) Wikipedia, zum Animieren bitte klicken
Using a Prism dispersion leads to splitting of white light beam into individual colors. A rainbow where light takes different paths inside the water dropplets, depending on their wavelength is another “real world” example of dispersion.
Every optical medium / glass type has different refraction indices for the various wavelength of light. The number that describes how different the light paths of the various wavelengths are, is the Abbe-number.
UNder dispersion formulas you find the most common formulas
Dispersion Formulas
Each optical material (glasses, plastics, gases) have a different refraction index for each wavelength.
Instead of keeping long tables, it’s possible to describe the behaviour of optical materials by formulas.
here are the main formulas used :
1: Sellmeier (preferred)
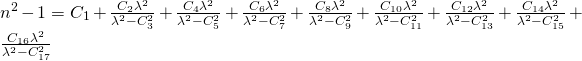
2: Sellmeier-2
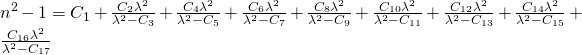
3: Polynomial
![]()
4: RefractiveIndex.info
![]()
5: Cauchy
![]()
6: Gases
![]()
7: Herzberger
![]()
8: Retro
![]()
9: Exotic
![]()
Distortion
see
Optical Distortion
TV Distortion
Optical Distortion vs. TV Distortion
Barrel Distortion
Pincushion Distortion